
The minimum Social Security benefit provision is an alternative benefit that increases benefits paid to low-income individuals.
Where the regular Social Security benefit formula bases the benefit amount on an individual’s lifetime earnings, the minimum Social Security benefit formula is based on the number of years a person has worked with earnings at or above a certain threshold.
The benefit amounts are still calculated through both formulas, but with the minimum Social Security benefit provision, the higher of the two benefits is the amount provided to qualified individuals.
In 2019, there were 64 million Social Security recipients; about 32,092 of them qualified for the minimum benefit. While it’s not a provision that impacts most people qualifying for Social Security, it’s still an important concept to understand if you want to broaden your full understanding of how the system works.
To start, let’s break down how benefits are normally calculated. Then, we can jump into the specific formula used for workers who fall under the minimum Social Security benefit provision umbrella.
How Social Security Benefits Are Normally Calculated
To be eligible for a Social Security retirement benefit, you must earn 40 credits. These “credits” equate to quarters of coverage, or years in which you earned income subject to Social Security taxes.
In 2023, you receive one credit for each $1,640 of covered earnings, up to a maximum of four credits per year. The amount of earnings needed to earn a credit increases annually as average wage levels increase.
When the Social Security Administration calculates the benefit for those who have earned the sufficient number of credits, they start by inflating your historical earnings.
The formula indexes each year of earnings to reflect historical wage growth using the Average Wage Index. Then, the formula divides the sum of your highest 35 years of indexed earnings by 420 (which is the number of months in 35 years).
If an individual has fewer than 35 years of covered earnings, years of no earnings get entered into the formula as zeros.
This calculation provides the inflation-adjusted average indexed earnings expressed as a monthly amount. Said another way, that’s your average indexed monthly earnings. The Social Security Administration (and the SSA website) will frequently refer to this figure by its acronym AIME.
Next, the calculation applies your AIME figure to the Social Security benefits formula that is in place the year you attain age 62.
Two numbers called “bend points” make up the benefits formula, which creates three separate bands your average income falls into to determine your benefit amount:
- For earnings that fall under the first bend point, you multiply by 90%. That is the first part of your benefit.
- For earnings that fall between the first and second bend point, you multiply by 32%. That is the second part of your benefit.
- For earnings that are greater than the second bend point, you multiply by 15%. This is the third part of your benefit.
The result of this formula is your primary insurance amount (PIA) which is also known as your full retirement age (FRA) benefit.
How the Minimum Social Security Benefit is Calculated
The calculation to determine the minimum Social Security benefit does not rely on a calculation based on an individual’s specific earnings history. Instead, it uses a person’s “years of coverage” to establish a minimum Social Security payment.
To determine the years of coverage an individual has, a certain threshold is used. As long as there were at least 11 years of earnings that were in excess of that threshold, a minimum benefit can be paid to that individual and their eligible family members. 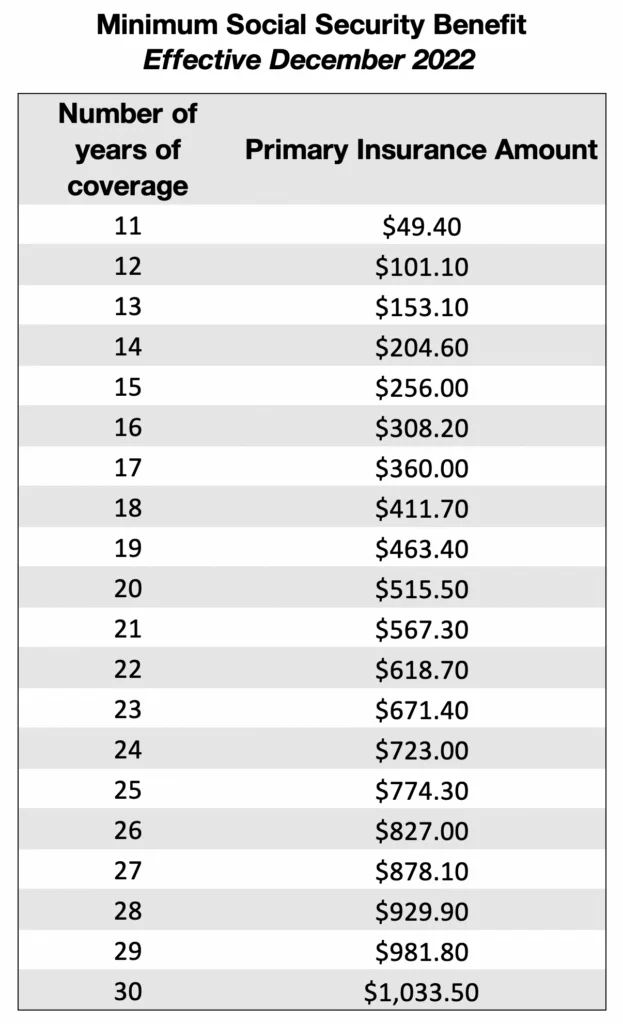
The amount of the benefit which can be paid is contingent on the number of earnings years which were over the threshold. In December of 2022, an individual with 11 years of coverage would have a benefit of $49.40 while an individual with 30 years of coverage would have a benefit of $1033.50.
You can see the following chart to see the PIA based on specific years of coverage:
What is the Minimum Social Security Benefit at Age 62?
The age-based impacts for the minimum Social Security benefit are nearly identical to regular benefits, with one big exception: There are no increases in benefits for delaying filing beyond your full retirement age.
However, the decreases for filing early still apply. Currently, benefits are reduced as follows if you file for your minimum benefit before reaching your FRA:
- If you file during the 36 month period prior to reaching your FRA, your minimum Social Security benefit will decrease by .555% per month
- If you file anytime before the 36-month period ahead of reaching your FRA, your benefit decreases by .417% per month.
Imagine that an individual who attained full retirement age at 67 had enough years of coverage to qualify for the full minimum Social Security benefit of $1,033. If they filed at 62, there would be a 30% reduction to benefits. This means that for 2023, the minimum Social Security benefit at 62 is $723.
What About Spousal Benefits, Survivors’ Benefits or Children’s Benefits?
As it relates to benefits for eligible family members, the minimum benefit works just like a regular benefit.
This means that your eligible spouse and children can also receive benefits based upon your work subject to the family maximum.
Technical Details of the Minimum Social Security Benefit
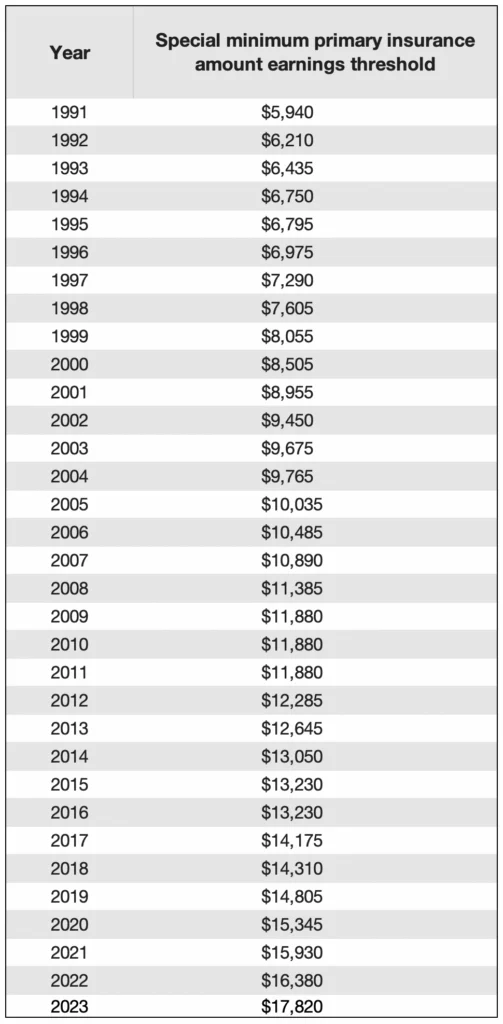
If you want to understand the technical details of how this annual threshold amount is determined, it’s based on the average wage index and the Old-Law Contribution and Benefit Base.
The Old-Law Contribution and Benefit Base is the maximum taxable earnings base that would have been effective without the enactment of the 1977 amendments to the Social Security Act.
To calculate the Old-Law Contribution And Benefit Base, use the following formula:
(AWI from two years ago / 1992 AWI) x $45,000 (1994 old-law base)
Since 1991, a year of threshold earnings used for the calculation of the minimum Social Security benefit is equal to 15% of the current old law base. For years prior to 1991, see the SSA’s threshold table.
Still Have Questions?
If you still want to learn more, You should also consider joining the nearly 400,000 subscribers on my Social Security Intelligence YouTube channel! This is where I break down the complex rules and help you figure out how to use them to your advantage.
Lastly, be sure to get your FREE copy of my Social Security Cheat Sheet before you go. This is where I took the most important rules and things to know from the 100,000 page Social Security website and condensed it down to just ONE PAGE! Get your FREE copy here.

[…] What is the Minimum Social Security Benefit? – Social … […]
[…] What is the Minimum Social Security Benefit? – Social … […]
[…] https://www.socialsecurityintelligence.com/what-is-the-minimum-social-security-benefit/ […]
[…] https://www.socialsecurityintelligence.com/what-is-the-minimum-social-security-benefit/ […]
[…] What is the Minimum Social Security Benefit? […]
[…] https://www.socialsecurityintelligence.com/what-is-the-minimum-social-security-benefit/ […]
[…] What is the Minimum Social Security Benefit? […]
[…] What is the Minimum Social Security Benefit? […]
[…] of the Social Security 2100 Act is the increase to the minimum Social Social Security benefit. This minimum benefit is the lowest amount an individual can receive who worked a certain number of years. It’s […]
What the hell does any of this mean?